OpenAPI
OpenAPI
Connect AI supports the OpenAPI specification version 2.0 and 3.0, allowing you to connect no-code/low-code applications that integrate with OpenAPI easily. Connect AI allows you to download an OpenAPI document from a workspace.
Generate an OpenAPI file for a Workspace
You can generate an OpenAPI specification file for a selected workspace. This file can be used in client applications to integrate with Connect AI via OpenAPI.
To generate an OpenAPI specification file:
-
In the dashboard, select Workspaces.
-
Select the workspace in which to generate an OpenAPI specification file. This file can be used in client applications to integrate with Connect AI via OpenAPI.
-
In the top menu, click View Endpoints.
An Endpoints dialog appears.
-
Select the OpenAPI tab.
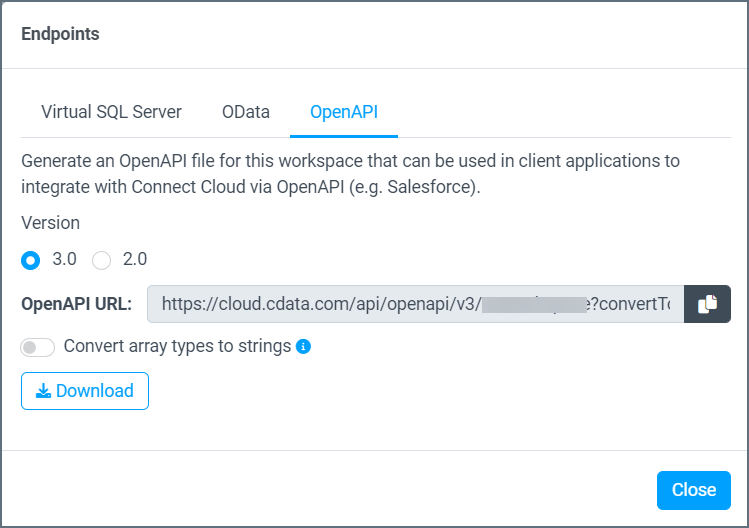
-
Select version 3.0 or 2.0 of OpenAPI.
-
Toggle Convert array types to strings on if the client application does not support array types (such as Microsoft Power Apps).
-
Click Download to download the OpenAPI specification file for the workspace. This is the file that is imported into the client application.
Note: Some integration tools accept an OpenAPI URL instead of the downloaded specification file. In that case, copy the OpenAPI URL in this dialog. Refer to the integration tool documentation for details.
-
Click Close.
Important: If a table’s schema within a workspace is modified (columns added or removed), you need to regenerate the OpenAPI specification file for the table’s workspace and re-import it into the client application.
API Operations
For each entity EntityName that is exposed in a data set, OpenAPI makes the following operations available. The inputs for each operation are described in the sections below.
-
ListEntityName
-
GetEntityName
-
CreateEntityName
-
DeleteEntityName
-
UpdateEntityName
-
GetCountEntityName
ListEntityName
The List operation invokes a GET request for all entities in the data set. The following are the inputs available for List:
-
$top=Nincludes only the first N records in the result. For example,$top=10returns only the top ten records in the entity. -
$skip=Nskips the first N records from the result. For example,$skip=10skips the first ten records in the entity, and begins with the eleventh record. -
$filterapplies OData operators, such asgt(greater than) oreq(equals) to the entities in the data set. See $filter for a complete list of operators. -
$orderbysorts the records in the entity by a property or properties. Separate the properties by a comma. You can sort byasc(ascending) ordesc(descending). The default value isasc. For example, order the data set byModel(ascending) and then byColor(descending) as follows:$orderby=Model asc, Color desc. -
$selectretrieves a subset of properties. For example, return the propertiesIdandModelfor all records in the data set as follows:$select=Id, Model.
GetEntityName
The Get operation invokes a GET request for an entity in the data set. The following are the inputs available for Get:
Id(or other primary key) is the unique identifier for the requested entity in the data set.
CreateEntityName
The Create operation invokes a POST request to add an entity to the data set. The following are the inputs for Create:
bodyis the body of the POST request, containing the properties of the entity.
DeleteEntityName
The Delete operation invokes a DELETE request to delete an entity. The following are the inputs for Delete:
Id(or other primary key) is the unique identifier for the requested entity to delete.
UpdateEntityName
The Update operation invokes a PATCH request to update an entity. The following are the inputs for Update:
-
Id(or other primary key) is the unique identifier for the requested entity to update. -
bodyis the body of the request, containing the properties of the entity to update.
GetCountEntityName
The GetCount operation invokes a GET request to get the number of the resource. The following are the inputs for GetCount:
$filterapplies OData operators, such asgt(greater than) oreq(equals) to the entities in the data set. See $filter for a complete list of operators.